Super Soil: Definition, Ingredients & Properties
Super soil represents a specially designed fertiliser mix which provides complete plant support from seed to harvest without the need for supplemental nutrients. This mixture includes compost and worm castings together with natural additives and beneficial microorganisms. The complete nutrient supply of super soil differs from traditional potting mixes that need periodic liquid feeding. The natural framework of super soil enhances both soil quality and plant growth strength. The combination of nutrients in super soil has made it popular among organic growers since they prefer natural cultivation methods without chemicals. The primary difference between traditional potting mixes and super soil involves drainage and texture compared to complete nutrient content and biological life, which enable self-maintenance for exceptional plant development.
Table of Contents
What are the Key Ingredients in Super Soil?
The key ingredients in super soil can be categorised into 4 groups:
- Base Components
- Amendments
- MacroOrganisms
- Microorganisms
Base Components
Here are 5 types of base materials used in super soil:
- Compost
- Peat Moss
- Coco Coir
- Worm Castings
- Topsoil
Compost
The compost consists of organic matter that has decomposed and is rich in nutrients. Soil structure receives benefits from compost, which also raises microbial activity and enhances water retention. Gardeners implement compost as a natural plant-feeding method to substitute synthetic chemical fertiliser products. People use organic kitchen waste together with leaves and grass clippings to produce compost, which creates a green solution for creating healthy soil that produces better yields.
Peat Moss
Peat bogs serve as the natural habitat for collecting the organic material known as peat moss. This material keeps water successfully with outstanding results, and it assists heavy soils by becoming lighter, which supports root growth. The acidic nature of peat moss suits plant species requiring soil environments with decreased pH values. The soil aerates through worm activity, which results in reduced compaction and develops stronger plant health.
Coco Coir
Coco coir is made from the fibres found in coconut husks. This natural material is produced from the outer husk of coconuts. The material efficiently retains moisture and improves air circulation through the soil without experiencing structural collapse. This natural substance shows three beneficial properties through its neutral pH balance and resistance to bacterial and fungal growth, while also being sustainable. Gardeners normally add coco coir to their potting mixes because it creates lightweight spaces which retain water effectively for seeds and plant placement.
Worm Castings
Worm castings develop when earthworms produce their nutrient-filled waste substances. The natural breakdown of decomposing earthworms adds essential mineral nutrients of nitrogen and phosphorus, and potassium to soil. The application of worm castings enhances both soil texture quality and improves water maintenance, and plants become more resilient. Organic gardeners strongly value this organic fertiliser because it enhances microbial activity, together with root health.
Topsoil
The top layer of soil, called topsoil, contains numerous nutrients and organic content. This layer supports plant development through its assistance to root growth, combined with its support for microbial populations. Topsoil with excellent quality features capabilities for proper water drainage while maintaining sufficient water content. The product serves essential functions during landscaping operations and in gardening work, and in lawn development activities.
Amendments
The following are the 7 types of Amendments that are used in super soil:
- Bone Meal
- Blood Meal
- Fish Meal
- Bat Guano
- Kelp Meal
- Rock Dust
- Dolomite Lime
Bone Meal
The manufacturing process of bone meal as a slow-release fertiliser begins with animal bone grinding. Bone meal functions as a fertiliser that contains abundant quantities of phosphorus and calcium to promote both roots’ healthy development and flowering abilities. There are two principal uses of bone meal in organic gardening since it enhances the structure of the soil while building up plant health through the development of sturdy stems and colourful blooms.
Blood Meal
Blood meal serves as a fertiliser for plants because it contains abundant amounts of nitrogen in dried animal blood form. When applied to the ground, the substance promotes lush foliage and creates intensely green-colored leaves for plants. Soil fertility benefits from using blood meal, which specifically enhances the growth of plants requiring elevated nitrogen levels. The quick response time of this fertiliser makes it ideal to use on depleted soils, where it delivers rapid growth enhancement for plant development.
Fish Meal
The agricultural industry produces fish meal through the grinding process of fish remains into a natural fertiliser. The fertiliser delivers vital soil nutrients that include nitrogen, together with phosphorus, as well as trace mineral compounds. Fish meal enables vibrant plant development while sustaining root system strength, along with maximising flowering productivity. The activity of soil microbes enhances when fish meal is present, thus plants receive better nutrient access, which produces stronger and healthier outcomes over multiple growing seasons.
Bat Guano
Bat guano represents an effective organic fertiliser containing high concentrations of nitrogen alongside phosphorus and potassium. The fertiliser originates from bat droppings collected from accumulation sites, which both nourish the soil and enhance microbial growth. Such organic fertiliser enhances both fruit development and root health, together with increased flowering capabilities. Plants receive performance-enhancing effects, furthermore environmental protection from the easy soil incorporation of this fertiliser.
Kelp Meal
The production of kelp meal occurs when seaweed is dried before grinding it into powder form. Because of its composition, kelp meal provides trace minerals along with growth hormones and enzymes that make plants healthier. Checking plants with kelp meal strengthens root systems while boosting their resistance to environmental stress and leads to improved plant life. Plants thrive better because kelp meal enhances soil structure and increases water retention while providing an organic method to feed plants naturally.
Rock Dust
The application of volcanic rock dust in its finely crushed form provides many soil minerals because it reintroduces a comprehensive mineral collection into the earth. The application of this material adds necessary elements, including calcium, iron, and magnesium, to restore soil health. Plants become stronger through the use of rock dust, which helps them develop better cell structures and builds up their resistance capabilities. The increased microbial activity in soils becomes possible through rock dust application, which results in healthier conditions for microorganisms.
Dolomite Lime
The mineral compound known as dolomite lime contains both calcium carbonate together with magnesium carbonate. Using dolomite lime results in a rise in soil pH that changes acidic conditions into neutral conditions. Plant development benefits from essential calcium and magnesium, which dolomite lime contributes to the soil foundation. When applied periodically, dolomite lime enhances root strength while simultaneously providing healthier foliage, together with balanced nutrient quantities in the soil.
MacroOrganisms
Here are 3 types of macroorganisms that are used in super soil:
- Earthworms
- Insects & Arthropods
- Other Beneficial Macrofauna
Earthworms
Earthworms are important soil organisms because they consume decaying plant debris to produce valuable nutrient-filled castings. When earthworms dig into the ground, they create openings which enhance air availability and water penetration. The natural tilling of the soil through earthworm action leads to improved root health and soil fertility, together with enhanced plant health, which requires no mechanical intervention or chemical fertilisers.
Insects & Arthropods
The decomposition process of organic matter receives assistance from insects and arthropods, which include ants and beetles. Through their movement through the soil, these organisms create better air circulation and enhance the recycling of necessary nutrients. The decomposition process accelerates through their activity, along with maintaining ecosystem balance as they improve natural soil structure.
Other Beneficial Macrofauna
Soil ecosystems benefit from various helpful macrofaunal species, including mites as well as centipedes and millipedes. The organisms consume both dead organic substances together with small pests while providing decomposition services and pest management benefits. The ecosystem functions better because macrofauna regulates soil balance while increasing nutrient cycling, which provides nutritious living conditions for plant roots.
Microorganisms
Below are the 3 types of microorganisms that are used in super soil:
- Bacteria
- Fungi
- Other Microbes
Bacteria
The bacteria in the supersoil convert organic substances into simple plant nutrients through decomposition. Soil bacteria contribute to nitrogen fixation together with vital nutrient recycling functions, and they sustain the overall health of the soil environment. When beneficial bacteria tie themselves to plant roots, they build stronger container roots that defend plants against natural diseases while making roots healthier.
Fungi
Mycorrhizal fungi, together with other fungi, create extensive networks which allow plant roots to collect additional water and nutrients. The organisms break down complex organic substances to release the necessary mineral nutrients, which plants need to thrive. The presence of fungi inside soil provides root protection against diseases while simultaneously offering drought resistance and improved support to the overall structure of the soil environment.
Other Microbes
Actinomycetes and protozoa, together with other microbes, function to enhance soil quality by decomposing organic materials and restraining damaging organisms. These microorganisms release nutrients from unavailable sources by enriching biological life while keeping all underground systems in balance. They produce ongoing biological processes which create a growing medium that becomes healthier and productive, and richer in quality.
What are the Properties of Super Soil?
The following are the 7 major properties of Super Soil:
- pH Level
- Nutrient Composition (NPK)
- Microbial Life
- Texture
- Water Retention
- Aeration
- Organic Matter Content
pH Level
The pH value of Super Soil ranges from 6.0 to 7.0, which functions optimally for almost every plant species. The benefits of this balanced condition make it possible for plants to take in nutrients and maintain proper microbial operations. Healthy mineral absorption happens when plants operate within the proper pH range because this condition prevents essential mineral lockout. A proper soil pH range from 6.0 to 7.0 enables both strong plant health and nourished biological functions within the soil ecosystem.
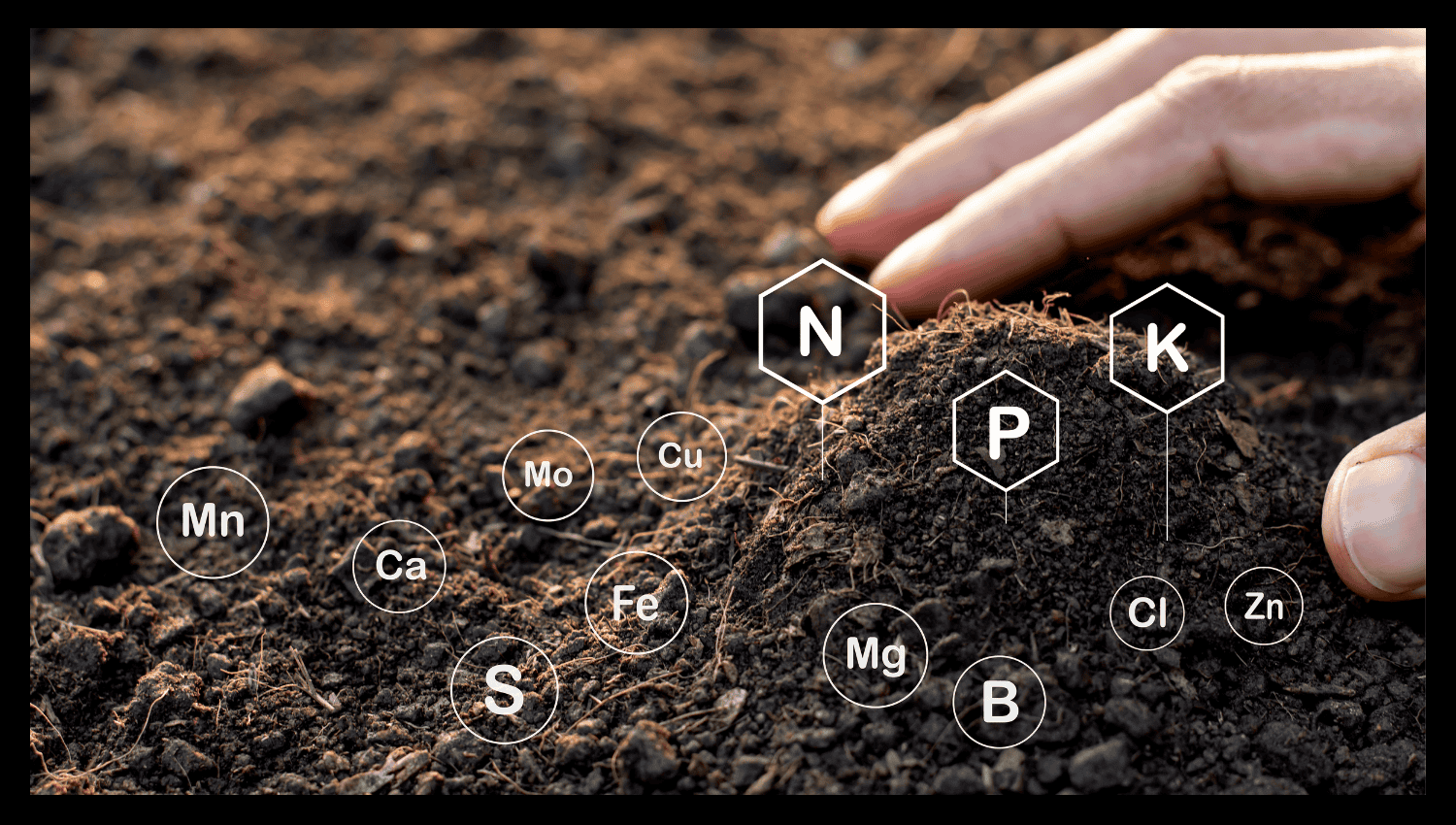

Nutrient Composition (NPK)
Super soil beneficially distributes three essential plant nutrients, nitrogen (N), together with phosphorus (P) and potassium (K). The primary nutrients help plants develop strong aboveground parts and robust roots while enabling successful flowering. The mixture contains essential micronutrients as well as NPK nutrients. The stable nutrition levels from this release system make chemical fertilisation unnecessary by supporting plant health at every development phase.

Microbial Life
Super soil teems with beneficial bacteria, fungi, and other microorganisms. The microbes transform organic materials into compounds which plants can take up nutrients from. Active microorganisms activate better soil health while giving plants disease resiliency and efficient nutrient recycling capability. Super soil receives its sustainable fertility quality from the microbial community that drives healthy natural plant development.
Texture
Super soil has a soft, loose texture, which enables roots to break ground effortlessly. The mix of both fine and rough materials in super soil creates an optimal structure which prevents soil reduction and enables the right water and air movement. Excellent soil texture enables plants to develop powerful root networks, which improves their ability to absorb nutrients, together with their capacity to survive adverse environmental conditions in weak soils.
Water Retention
Supersoil contains enough water reserves to support plant growth while avoiding saturated conditions. Super soil contains organic ingredients, including compost, together with coco coir that enhances water retention in the soil without creating waterlogged conditions. A properly balanced water content allows roots to maintain consistent moisture levels, which protects crops from drought stress and helps them grow better and disease-free.
Aeration
Super soil maintains perfect air circulation, which is fundamental for proper plant and microbial development. The incorporation of perlite or pumice creates air pockets which spread throughout the soil. The oxygen needs of roots become possible with good aeration, which enhances nutrient acquisition as it supports a healthy microbial ecosystem. Plants develop into strong, fast-growing entities with better strength when the soil provides proper air circulation.
Organic Matter Content
Super soil receives its organic substance from compost alongside worm castings and decomposed plant waste. Beneficial soil microbes receive nutrients from organic matter while they also work to develop soil structure and deliver nutrients at a controlled pace. Soil fertility is strengthened by high organic matter levels and improved water retention and air circulation. It produces a self-sustaining flourishing garden system for plants to flourish naturally without chemical additives.