The Nutritional and Microbial Makeup of Soil in Cannabis Cultivation
Cannabis cultivation is both an art and a science, requiring a deep understanding of environmental factors that influence plant growth. One of the most critical yet often overlooked components of successful cannabis cultivation is the soil. The soil serves as the foundation for the plant’s root system, providing essential nutrients, water, and a habitat for beneficial microbes. A well-balanced soil not only supports vigorous growth but also enhances the plant’s ability to produce high-quality flowers with rich cannabinoid profiles.
In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the complex interactions between the nutritional and microbial makeup of soil and how these elements affect cannabis growth. We will explore the specific nutrient requirements of cannabis, the role of beneficial microbes, soil management practices during different growth stages, common soil-related issues to watch out for, and ten best practices for developing and managing soil effectively. Whether you’re a home grower or a commercial cultivator, understanding the intricacies of soil can significantly improve your yields and overall plant health.
Nutritional Composition of Soil for Cannabis Cultivation
Healthy soil is the cornerstone of robust cannabis cultivation. Cannabis plants require a balanced mix of macronutrients and micronutrients, each serving unique roles in plant development. A deficiency or excess of any nutrient can lead to suboptimal growth and reduced yields. Proper nutrient management is essential throughout the plant’s life cycle to ensure healthy development and maximize yields.
Macronutrients
Macronutrients are the primary building blocks that cannabis plants require in large quantities. These include:
1. Nitrogen (N): Crucial during the vegetative stage, nitrogen supports leaf and stem development. It is a fundamental component of chlorophyll, the molecule responsible for photosynthesis. A nitrogen deficiency can lead to yellowing leaves and stunted growth, while an excess can cause overly lush foliage at the expense of bud production.
2. Phosphorus (P): Vital during the flowering stage, phosphorus supports root development and flower production. It plays a key role in energy transfer within the plant. Deficiencies can result in poor bud formation, discolored leaves, and weak root systems.
3. Potassium (K): Essential for overall plant health, potassium aids in water uptake, enzyme activation, and disease resistance. It helps regulate the plant’s internal processes, including the opening and closing of stomata. A lack of potassium can lead to weak stems, leaf curling, and increased susceptibility to pests and diseases.
Maintaining the right balance of these macronutrients is critical for optimal growth and high yields.
Micronutrients
Micronutrients, though needed in smaller quantities, are equally vital for cannabis growth. These include:
– Calcium (Ca): Strengthens cell walls and aids in nutrient uptake. A deficiency can cause distorted leaves and blossom end rot.
– Magnesium (Mg): A core component of chlorophyll, necessary for photosynthesis. Magnesium deficiencies manifest as interveinal chlorosis.
– Sulfur (S): Important for protein synthesis and enzyme function. Deficiencies lead to yellowing of new growth.
– Iron (Fe), Manganese (Mn), Zinc (Zn), Copper (Cu), Molybdenum (Mo), and Boron (B): Each plays specialized roles in enzymatic reactions, chlorophyll production, and nutrient transport. Deficiencies in these micronutrients can lead to a variety of growth abnormalities and reduced yields.
Understanding the role of micronutrients and how they interact with macronutrients is essential for maintaining plant health.
The Importance of Soil pH in Nutrient Uptake
Soil pH plays a crucial role in the availability of nutrients to cannabis plants. The ideal pH range for cannabis is between 5.8 and 6.5. When the pH deviates from this range, certain nutrients become less available, leading to deficiencies even if the soil contains adequate amounts. Regular monitoring and adjustments using pH up or down solutions can help maintain optimal levels, ensuring your plants can access all the nutrients they need.
A well-balanced pH not only supports nutrient uptake but also promotes a healthy microbial environment in the soil, which further aids in nutrient absorption.
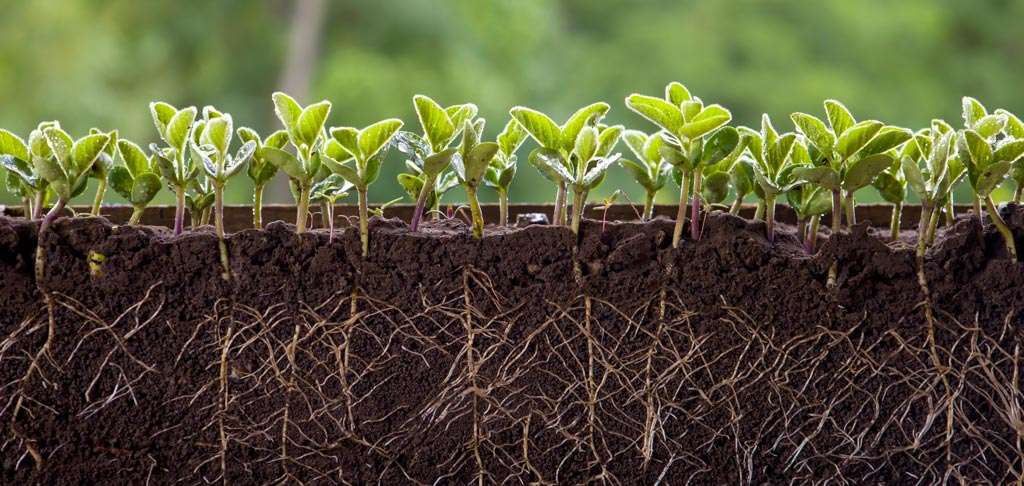

Microbial Makeup of Soil
Soil microbes form a complex ecosystem that supports plant health by enhancing nutrient availability, protecting against pathogens, and improving soil structure. Beneficial microbes play a crucial role in the soil food web, breaking down organic matter into forms that plants can readily absorb. Healthy microbial activity in the soil leads to more efficient nutrient cycling and can significantly boost plant growth and yield.
Mycorrhizal Fungi
These symbiotic fungi colonize plant roots, extending their hyphae into the soil to access water and nutrients beyond the reach of roots alone. In return, they receive carbohydrates produced by the plant. Mycorrhizal associations are particularly beneficial for cannabis, enhancing phosphorus uptake, improving drought resistance, and increasing overall plant vigor. Studies have shown that cannabis plants inoculated with mycorrhizal fungi exhibit stronger root systems and higher yields.
Including mycorrhizal inoculants in your soil mix can greatly improve the efficiency of nutrient uptake and overall plant health.
Beneficial Bacteria
Beneficial bacteria like Bacillus subtilis and Pseudomonas fluorescens play key roles in soil health. They decompose organic matter, fix atmospheric nitrogen, and produce natural antibiotics that protect roots from harmful pathogens. These bacteria create a biofilm around roots, enhancing nutrient absorption and boosting plant immunity. Other bacteria, such as Rhizobium species, form symbiotic relationships with legumes, fixing nitrogen into the soil, which can benefit cannabis when grown as part of a crop rotation system.
A thriving bacterial community in the soil is essential for maintaining soil health and ensuring your cannabis plants receive the nutrients they need.
Soil Amendments and Enhancements
Soil amendments are materials added to the soil to improve its physical or chemical properties. Common soil amendments used in cannabis cultivation include:
– Compost: Adds organic matter and beneficial microbes.
– Worm Castings: A nutrient-rich amendment that promotes microbial activity.
– Perlite: Enhances soil aeration and drainage.
– Vermiculite: Improves water retention.
– Biochar: Increases nutrient retention and supports microbial life.
These amendments help create a well-balanced growing medium that supports robust plant growth and high yields.
Common Soil Problems and How to Fix Them
Even with the best practices, soil-related issues can arise during cannabis cultivation. Here are some common problems and how to address them:
– Nutrient Lockout: This occurs when nutrient absorption is hindered due to pH imbalances or salt buildup. Flushing the soil with pH-balanced water can help.
– Poor Drainage: Compacted or clay-heavy soils can retain too much water, leading to root rot. Adding perlite or sand can improve drainage.
– Pests and Pathogens: Soil can harbor harmful organisms. Regularly inspect plants and use organic treatments like neem oil or beneficial nematodes.
– Deficiencies: Yellowing leaves, stunted growth, or other symptoms may indicate nutrient deficiencies. Soil testing can help identify the issue and guide corrective actions.
Addressing these common soil issues promptly can help maintain plant health and maximize yields.

Case Study: Successful Cannabis Cultivation with Organic Soil
A cannabis farm in Northern California implemented organic soil practices and reported a 30% increase in yields over a single season. By focusing on high-quality compost, worm castings, and regular applications of mycorrhizal fungi, the farm created a nutrient-rich environment. Their soil testing revealed balanced pH levels and an abundance of beneficial microbes, resulting in healthier plants and more potent flowers.
The farm also implemented cover cropping during the off-season, which helped to maintain soil fertility and reduce erosion. By avoiding synthetic fertilizers and pesticides, they were able to produce a cleaner, more natural product that commanded higher prices in the market.
Advanced Soil Testing Techniques
Soil testing is an essential practice for cannabis cultivators who aim to optimize soil health and plant productivity. Advanced soil testing goes beyond basic pH and nutrient levels, analyzing soil texture, microbial activity, and organic matter content.
1. **Soil Texture Analysis**: Understanding the proportions of sand, silt, and clay in your soil can help tailor irrigation and nutrient management practices.
2. **Microbial Activity Testing**: Tests such as Solvita® measure soil respiration, indicating microbial health and activity levels.
3. **Organic Matter Analysis**: Determining the percentage of organic matter in your soil provides insights into its nutrient-holding capacity and overall fertility.
Regular soil testing allows growers to make data-driven decisions, ensuring optimal conditions for cannabis growth throughout the cultivation cycle.
Composting for Cannabis Cultivation
Composting is an eco-friendly way to recycle organic waste into nutrient-rich soil amendments. For cannabis cultivation, composting offers several benefits, including improved soil structure, enhanced microbial activity, and a steady release of nutrients.
**Composting Basics:**
– **Green Materials**: Rich in nitrogen (e.g., vegetable scraps, coffee grounds, grass clippings).
– **Brown Materials**: High in carbon (e.g., dried leaves, straw, cardboard).
– **Moisture and Aeration**: Maintaining the right moisture level and regularly turning the pile promotes aerobic decomposition.
**Benefits of Compost in Cannabis Cultivation:**
– Increases organic matter and improves soil structure.
– Enhances water retention and drainage.
– Boosts microbial diversity, supporting plant health.
Using high-quality compost as a soil amendment can significantly improve cannabis plant vigor and yields.
Sustainable Soil Management Practices
Sustainability is increasingly important in modern cannabis cultivation. Implementing sustainable soil management practices not only benefits the environment but also leads to healthier plants and better yields.
**Key Sustainable Practices:**
1. **Cover Cropping**: Planting cover crops like clover or rye during the off-season helps prevent erosion, improve soil structure, and fix nitrogen.
2. **Crop Rotation**: Rotating cannabis with other crops reduces soil nutrient depletion and disrupts pest and disease cycles.
3. **No-Till Farming**: Minimizing soil disturbance preserves soil structure, retains moisture, and protects beneficial microbial communities.
4. **Integrated Pest Management (IPM)**: Using natural predators, biological controls, and organic treatments to manage pests and diseases sustainably.
By adopting these practices, growers can maintain soil fertility, reduce reliance on synthetic inputs, and promote a healthier ecosystem.